OK, so I’m beyond excited to finally get to write this article. There’s been a lot of talk about how to optimize your site for ChatGPT but not a ton of data studies around it. However, in this article I want to change that. This article is a study of actual searches that ChatGPT performs so SEOs can all better understand what strategies will work to optimize for it.
Let’s do it!
The Background On ChatGPT Search
We know users are getting information off ChatGPT but there’s two different ways that ChatGPT actually gets that information:
- It answers the questions using it’s native knowledge
- It doesn’t know the answer so it performs a search. Here is uses the searches to ground the information it’s looking for.
Here’s a really simple example of a prompt where ChatGPT doesn’t know the answer natively, so it grounds in search:

There’s been a lot of debate about whether or not ChatGPT is using Google’s search index to do this or not. I personally think it does (here’s a great article on it), but that’s a discussion for a different day. What’s important to understand is that when ChatGPT uses search, SEOs have much more control over the information that’s presented. This is ChatGPT is basically a wrapper for search engines. So if we can figure out how often and what the LLM is searching, we’re going to have an easier time optimizing for it.
What’s cool is that you can actually see the queries inside of ChatGPT. There’s a process you can use to identify the JSON file that it returns where it will show you the queries used during a given search.
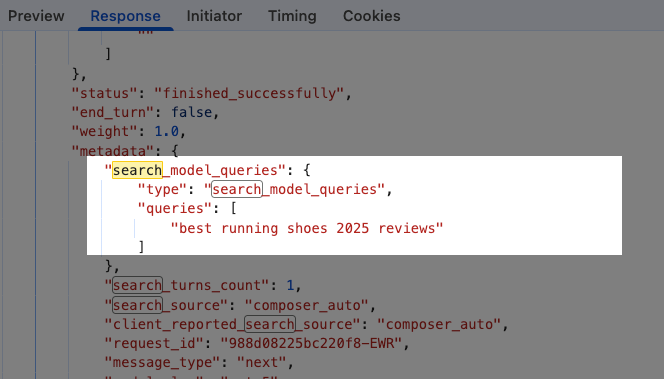
So the data is there, it’s just not super accessible. There are some tools like ChatGPT Search Capture that let you find the queries for an individual chat using just point and click. However, we haven’t had ways of extracting the data at scale…until now.
Extracting ChatGPT Fan-Out Data
This is where I have to give my co-founder at Nectiv Jason Melman some major props. He’s both an amazing SEO and developer which allows us to do some really cool things. The other week he approached me mentioning that he may have found a way to extract the queries from ChatGPT at scale. In just an afternoon, he was able to add functionality to our AI Tracker that allows us to examine the queries ChatGPT is using.
We immediately knew that we had to do this at a larger scale. Doing so would allow us to identify better trends to understand exactly how ChatGPT search queries work. After bugging Jason on Slack , we were able to upload 8,500 prompts through our AI tracker and extract ChatGPT’s fan out queries at scale.
Methodology
For this study, we analyzed 8,500+ prompts in Nectiv’s AI tracker. We then analyzed whether or not those prompts recorded a search and extracted all the search queries on ones that did. We looked at prompts against 9 different verticals: Beauty, Commerce, Credit Cards, Fashion, Jobs & Careers, Local, Software, Real Estate and Travel. For the analysis, we looked at both overall trends in the aggregate dataset and trends that were specific to these key verticals.
Please note that prompt tracking is already fuzzy. The goal of this study was to try to analyze how ChatGPT searches when someone has a commercial/buying intent (best women’s dresses, nyc to la flight). That way we can figure out what content we need to connect with these BOFU searches it performs.
ChatGPT Fan Out Query Key Findings
Alright, so let’s get into some of the findings from the analysis. First we can look at the aggregate numbers from ChatGPT:
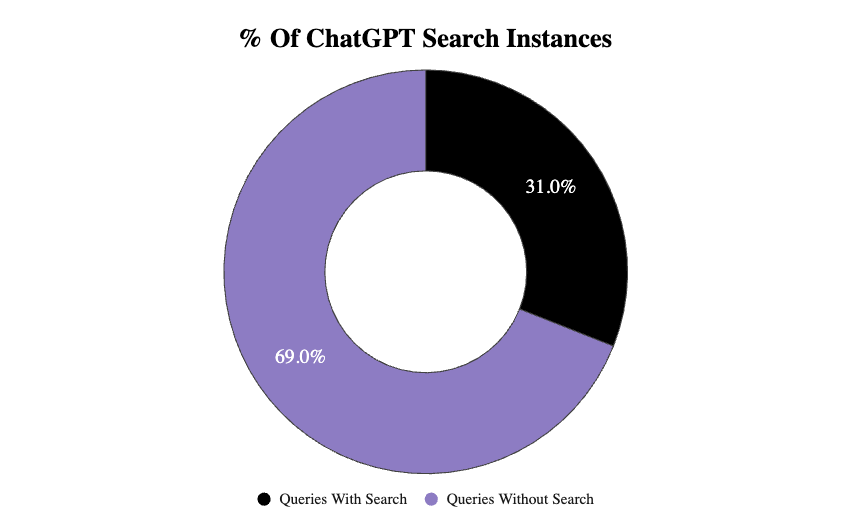
- Total Number Of Searches: 2,648
- Percentage Of Search Instances: 31%
- Average Number Of Searches: 2.17
- Average Words Per Query: 5.48
So almost one third of the time, ChatGPT is performing a search off a prompt in this dataset.
Across all verticals, it’s normally going to perform about two searches to identify the information. ChatGPT is also going to perform longer queries on average. It averages using between 5-6 words per search. For example, that means it’s searching things like “top car rental Turkey reviews” or “top bomber jacket brands”. So slightly longer than most of use are used to tracking and optimizing for.
How Many Fan Out Queries Does ChatGPT Use?
The concept of “query fan out” means that an LLM doesn’t always just perform one search. It can perform multiple. For example, Google is showcasing that their system will search across 8+ queries to identify information for users.
As we noted about, the average across the whole dataset was 2 searches. However, what’s interesting is when bucketing the number of searches it performs, three searches is actually the most common instance with 1,279 tracked instances.
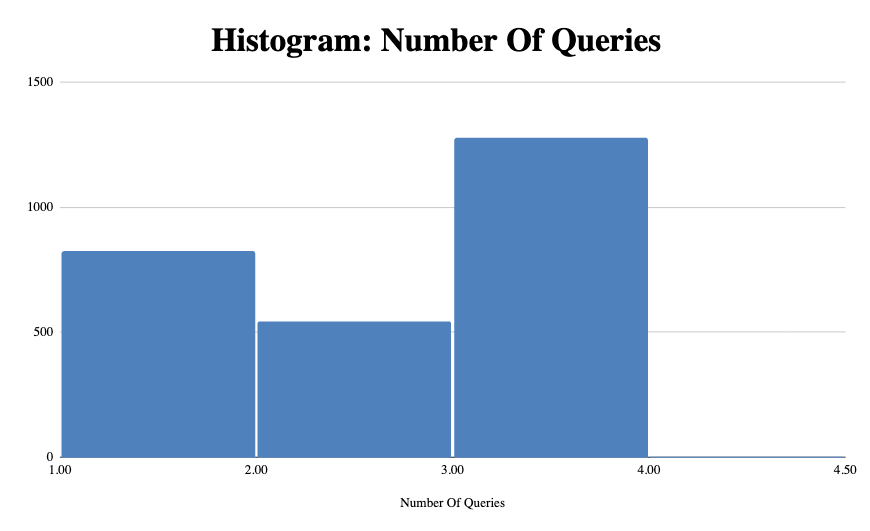
While you can’t see it in the data, there was a single recorded instance of four queries. That leads me to believe that ChatGPT maxes out at 4 query-fan outs at the most.
How Many Words Do Fan Out Queries Use?
So we know that on average, ChatGPT queries are longer with length on average of between 5-6 words, with an average of 5.48 words per query. A study by Semrush estimates that the average Google search is 3.4 words in the US. That means that ChatGPT’s search queries are 61% longer on average than a standard Google search.
But I don’t think that entirely does it justice when you look at the dataset. In fact, when you look at the data, the query lengths can skew even longer.
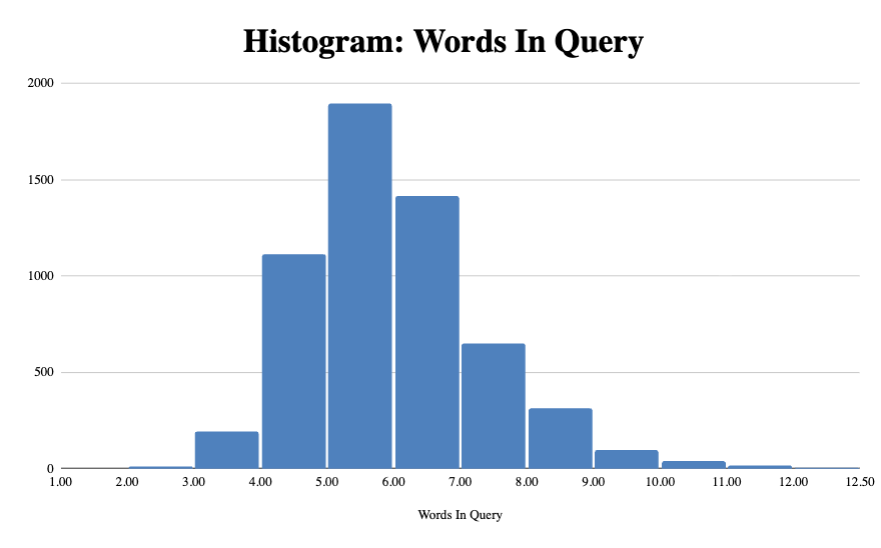
In fact, when grouping the queries together like this, you find that MOST of the queries tend to be longer. In fact, 77% of all the queries were 5 words or longer.
It’s also worth noting that the maximum query length the dataset was 12. A few examples included:
- ROOMS to go credit card pre approval rooms to go credit preapproval
- best interchange rate credit card USA interchange fee rates credit card issuer
- compare Razer Phone models Razer Phone 2 Razer Phone 1 user reviews
I’m not sure if that’s the limit but you’re unlikely to get search queries past 12 words in length.
How Frequently Does ChatGPT Use Search By Industry?
One thing we wanted to assess was how frequently ChatGPT uses the search function for different industries. All industries can’t be treated equally so we figured that some might have more aggressive search than others. We were able to segments all of our prompts to see trends for this:
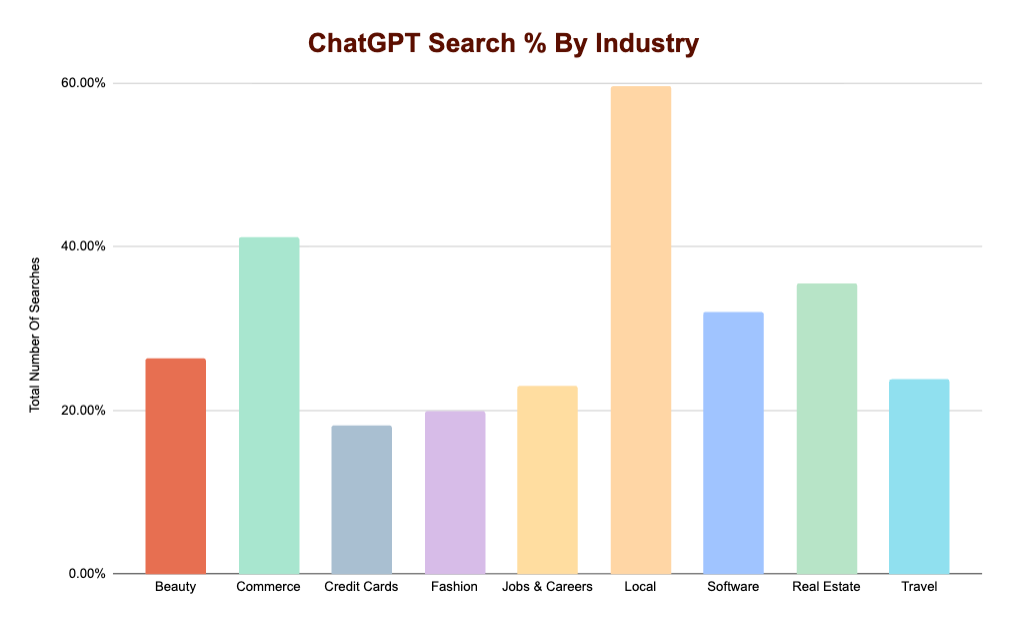
Some really interesting insights included:
- ChatGPT is using search AGGRESSIVELY for prompts with “Local” intent. Across our dataset it performed 565 searches and performed a query in 59% of all instances. So if you’re in local, ChatGPT is very likely using search to surface your information.
- General “Commerce” was also likely to utilize the search function, with ChatGPT triggering it 41% of the time.
- Credit Cards and Fashion were the least likely to have ChatGPT perform a search with only 18% and 19% of instances respectively.
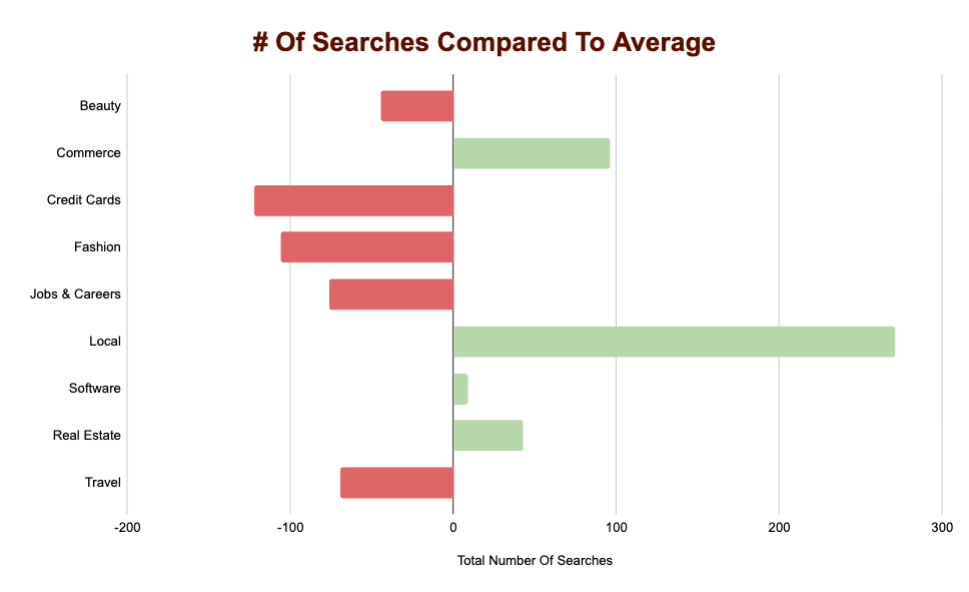
To make it easier to visualize, we also created this chart that shows how many more or fewer searches a vertical performed against the average:
How Do Query Fan Outs Change By Industry?
When we looked at the aggregate data, we found that ChatGPT averages about 2.1 queries for all the prompts we analyzed. We also wanted to see if there was a lot of variance when we broke it down by industry. Looking at the industries as a whole, we see that most industries seem to hover around that 2 query mark:
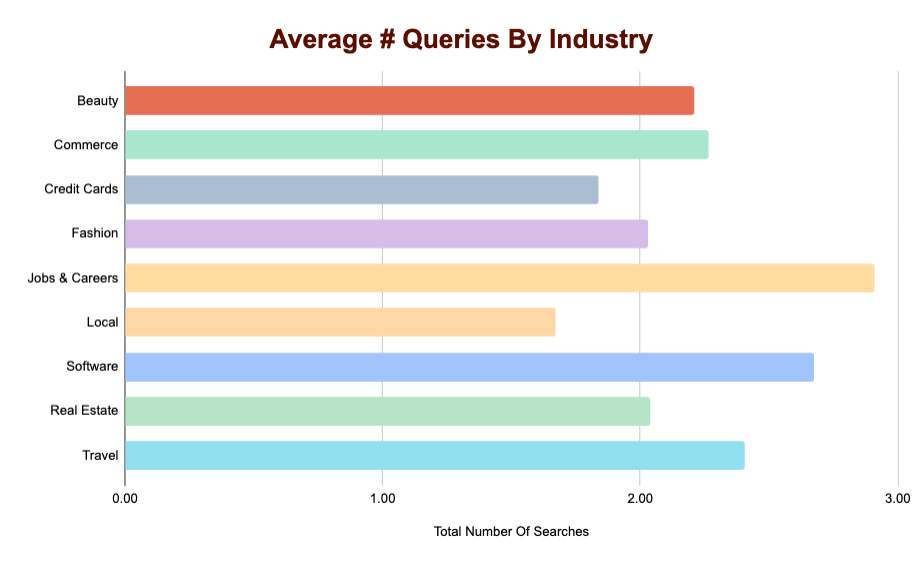
However, there was enough variance for some interesting takeaways:
- For Jobs & Careers, ChatGPT performs the most searches by bar, averaging nearly 3 searches across the dataset.
- Software also saw increased query-fan outs from the rest of the dataset with an average of 2.68 queries.
- While it searches the most number of instances in Local results, it actually average the FEWEST number of fan-outs. Local searches averaged 1.67 searches, the lowest of any vertical.
Does The Number Of Words In A Query Change By Industry?
Another interesting question we wanted to analyze is if the number words changed based on the industry. Does ChatGPT need to search longer tail queries for some industries but not others. The short answer seems to be no. For the time being, most industries get the 5-6 words per query.
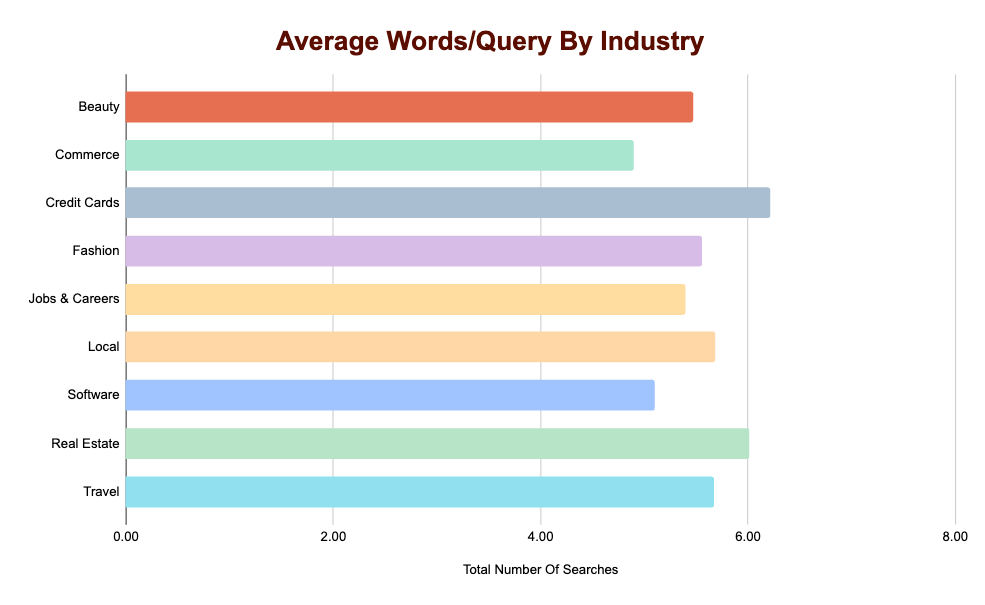
Credit Cards and Real Estate did have the highest number of words (6+).
What Types Of Queries Is ChatGPT Searching?
OK so this the most valuable section of the data but also the trickiest to analyze. The biggest reason is that what ChatGPT is inherently a function of the prompts that are put in. So naturally the data here skewed heavily towards the language I used in the prompts as well as the industries I decided to focus on. However there are some clear NGram patterns on how it searches that apply regardless of the prompts/industry you choose.
To do this, I used the following logic to filter to NGrams that would apply:
- The NGram or a synonym was not used in the original prompt
- The NGram appeared in at least 3 of the datasets.
Using this logic, below you can find the most common five NGrams across the entire dataset:
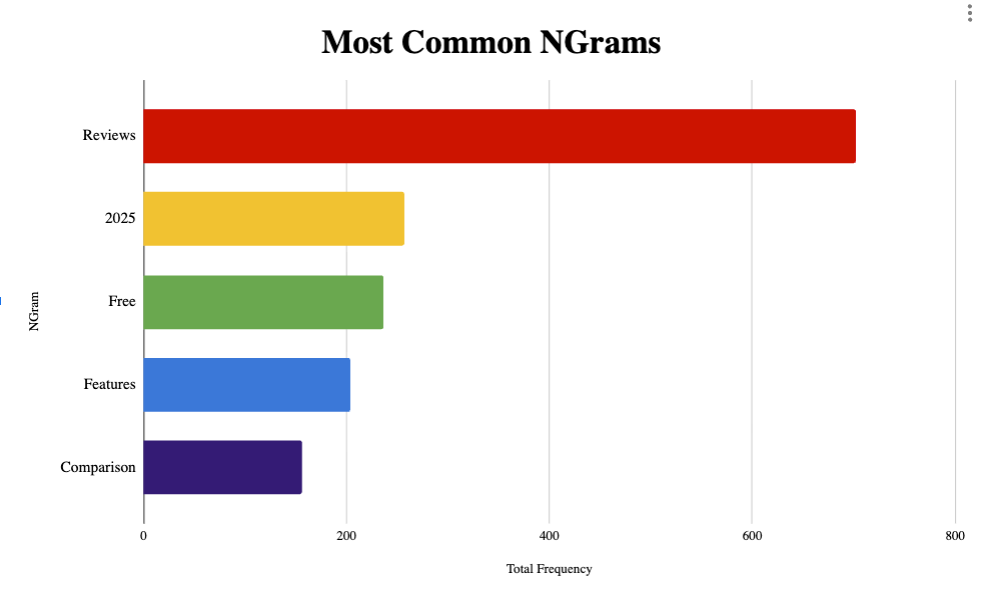
These are key findings as these are terms you’ll want to optimize your content for to connect with ChatGPT fan-out queries. Let’s analyze a few of them:
- Reviews: By far the most popular one with 702 instances. ChatGPT will often searches for reviews of products, services or software.
- 2025: ChatGPT is obsessed with freshness and current year. Like the standard ole SEO tactic of adding your year to title tags and updating them annually, this will likely help for ChatGPT visibility.
- Features: I thought this would only be in the “Software” dataset but it’s present across Commerce, Fashion and even Credit Cards. ChatGPT is using “features” terminology to learn about products (ASICS Gel Kayano 29 vs 30 features, Chase Sapphire Reserve features).
- Comparison: ChatGPT seems to want to connect with content that compares products (best ecommerce business software platforms comparison). Creating content that compares your product to others is likely a viable strategy.
Of course, these NGrams change based on what industry you’re looking at.
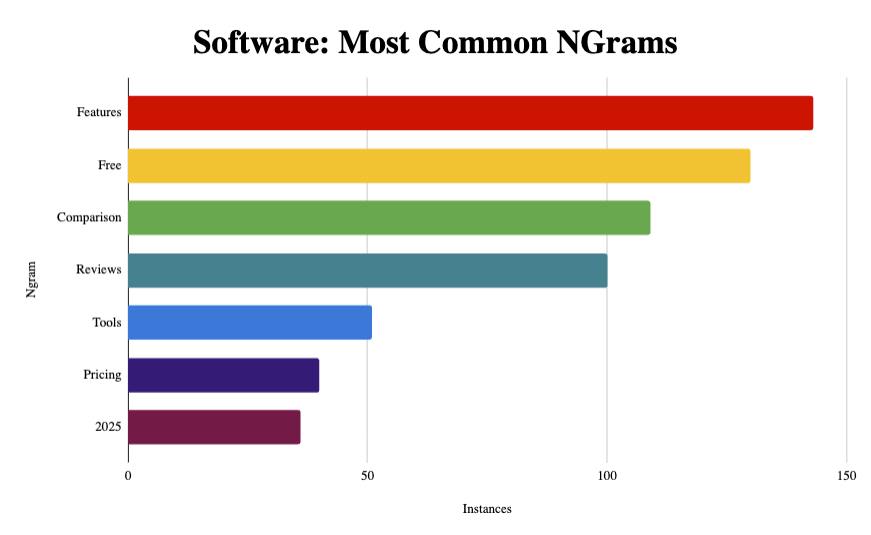
For instance, drilling down into Software I see emerging ones such as “Tools” and “Pricing”, while NGrams such as “Features” and “Free” are even more prominent.
If you want to know you’re particular site’s NGrams, feel free to reach out and we can identify some for you.
Conclusion
I hope this data is valuable to you. Knowing that we were able to extract, I almost felt a duty to the community to go out and try to analyze it so we can all understand how ChatGPT works. Hopefully this gives us all some insights on how we can better optimize against the future of search.
One note is that if you’re interested in better understand you’re own query-fan outs or visibility in the LLMs, feel free to reach out. We would get you set up with some initial tracking data for you to better understand your ChatGPT landscape.
Appreciate it all!
